Follow these steps to learn how to read an input signal.
Configuration
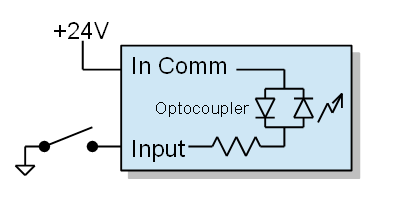
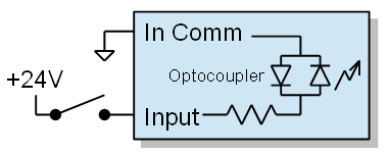
Inputs can respond to sourcing signals (PNP, switch closure to +24) or sinking signals (NPN, switch closure to ground). Examine your sensors and determine if the controller inputs need to respond to sourcing or sinking type. It is simplest if the sensors are all the same type. If the sensors are not a all the same type contact support for additional information to support your particular sensor configuration.
If you have sinking inputs then wire "In Comm" (Input Common) to 24 volts and your sensor to the input:
If you have sourcing inputs then wire "In Comm" (Input Common) to return and your sensor to the input:
Set Communication Parameters
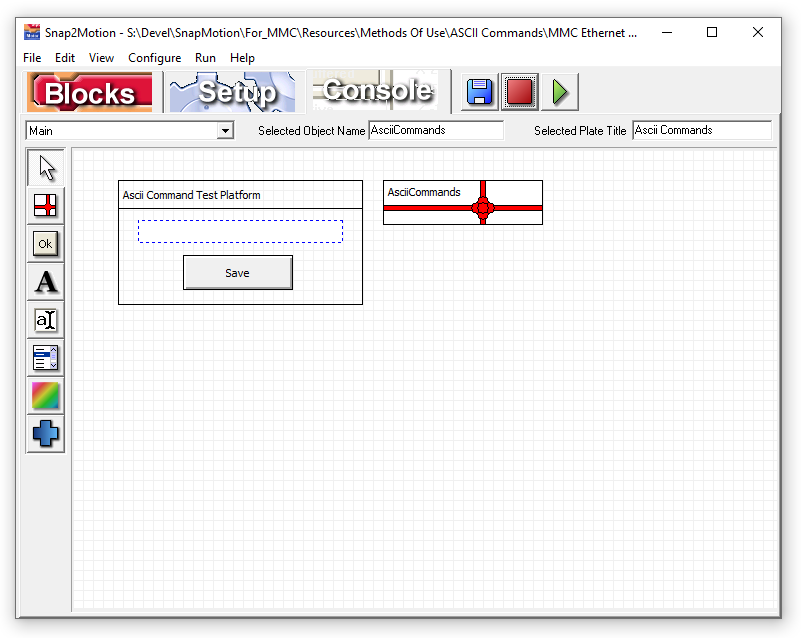
Select "File | Open Software Components..", go into the Methods Of Use directory and identify the type of Ascii Command Interpreter needed. Below is the view of the TCP/IP version:
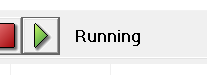
Click the "Play" button and wait for the status to indicate "Running":
Use "Ping" to Confirm Network Configuration
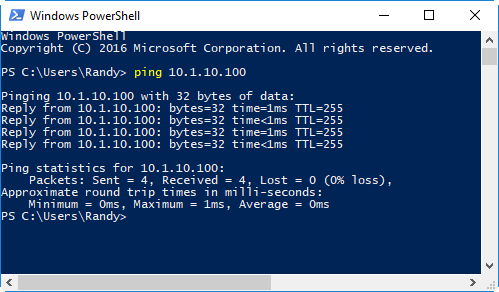
Once the program is running we can use the "ping" command to confirm that the PC is able to connect to the controller over TCP/IP. Open a command line or PowerShell and type in the ping command:
If you do not get a ping response confirm that you have a cable plugged in and are seeing the green activity lighto on the Ethernet connector. Confirm that the PC is on the same subneet with a non-conflicting IP address.
Use Telnet to Issue Commands
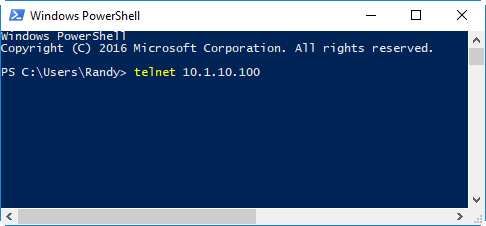
Confirm that you have your computer's IP address on the same subnet as what was chosen for the controller's IP address. Plug in an Ethernet cable and confirm that you see the characteristic green blinking light indicating Ethernet traffic. Open a command or Power Shell window and initiate a telnet session by providing the IP address:
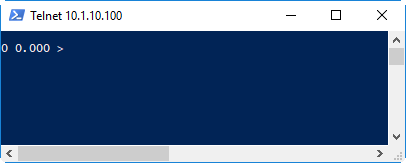
Press "Enter" and this is seen:
The first "0" indicates that no error occurred in handling the command. The second floating point 0 is the value of the response which in this nop command case is 0.
The MAC has two types of inputs. There are 18 optically isolated, sourcing-or-sinking style inputs as discussed as well as 48 points of TTL IO on the left 50 pin connector. To access the isolated IO use the command "ISI" followed by the bit number:
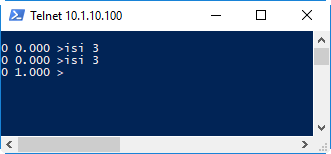
If the signal is not present the return result is 0 (no error) and 0.000 (no signal). If the signal is present the first response is 0 (no error) followed by 1.000 (signal present).
To reference the TTL input bits use the "INB" command followed by the bit number. TTL Inputs are internally pulled up so reading a disconnected signal returns a "1". Connect the signal to ground to produce a "0":

Additional commands and parameter details are the command reference section of the manual.